IoT trends 2025 sets the stage for a fascinating look at the future of interconnected devices. From emerging technologies to security concerns, and industry-specific applications, this exploration will unveil the key developments shaping the IoT landscape in the coming year. The impact on business, society, and global adoption will also be analyzed.
The rapid evolution of communication protocols, infrastructure advancements, and data management systems are critical components in understanding the comprehensive picture of IoT trends. This analysis also examines the profound influence of artificial intelligence, emphasizing its role in automating and enhancing IoT systems. A critical evaluation of ethical considerations will also be included.
Emerging Technologies in IoT
The Internet of Things (IoT) is rapidly evolving, with new technologies constantly reshaping its landscape. In 2025, several emerging technologies promise to significantly impact existing IoT applications, enhancing functionality, and driving innovation across diverse sectors. These technologies are not isolated advancements but rather interconnected, creating a synergy that is poised to revolutionize how we interact with and manage the world around us.These emerging technologies are poised to not only augment existing IoT applications but also create entirely new avenues for development and deployment.
They promise enhanced data processing capabilities, improved security measures, and more intelligent decision-making within IoT systems.
Promising New Technologies
Several new technologies are set to redefine the IoT landscape in 2025. These include advancements in edge computing, AI-powered analytics, enhanced security protocols, and the increasing adoption of blockchain technology. Each of these technologies brings unique strengths and potential weaknesses that will impact the future of IoT applications.
Impact on Existing IoT Applications
These emerging technologies will profoundly impact existing IoT applications. For example, edge computing will enable real-time data processing, leading to quicker responses and reduced latency in industrial automation and smart city applications. AI-powered analytics will enhance the ability of IoT systems to learn from data and predict future outcomes, leading to proactive maintenance and improved resource management. Enhanced security protocols will bolster the resilience of IoT networks, reducing vulnerabilities and mitigating risks associated with cyberattacks.
Comparison of Emerging Technologies
| Technology | Strengths | Weaknesses |
|---|---|---|
| Edge Computing | Reduced latency, enhanced privacy, improved scalability, and reduced reliance on centralized data centers. | Requires significant infrastructure investment, potentially increasing costs, and demands specialized expertise for deployment and maintenance. |
| AI-powered Analytics | Enhanced decision-making capabilities, improved predictive maintenance, and optimized resource management. | Potential for bias in algorithms, requires significant data sets for training, and raises ethical concerns about data privacy and security. |
| Enhanced Security Protocols | Increased resilience to cyberattacks, enhanced data protection, and improved trust in IoT systems. | Increased complexity in implementation, potential for vulnerabilities in new protocols, and requires continuous monitoring and updates. |
| Blockchain Technology | Improved data integrity, enhanced transparency, and secure data sharing across various devices and applications. | Scalability issues can limit its application in some scenarios, and complex implementation can lead to high costs. |
Potential Use Cases Across Industries
The transformative potential of these emerging technologies is widespread.
- Smart Agriculture: Edge computing can process sensor data in real-time to optimize irrigation schedules and predict crop yields. AI-powered analytics can identify patterns indicative of disease or pest infestations, enabling proactive intervention. Blockchain technology can create secure and transparent supply chains for agricultural products.
- Smart Cities: Edge computing can enable real-time traffic management and optimize traffic flow, reducing congestion and improving efficiency. AI-powered analytics can predict energy consumption patterns, optimizing energy grids and resource allocation. Enhanced security protocols can protect critical infrastructure and prevent cyberattacks.
- Industrial Automation: Edge computing can enable real-time monitoring and control of industrial processes, leading to improved efficiency and reduced downtime. AI-powered analytics can predict equipment failures and optimize maintenance schedules. Blockchain technology can track and verify the authenticity of parts and components, ensuring quality and reducing fraud.
Security Considerations for IoT in 2025
The Internet of Things (IoT) is rapidly expanding, connecting billions of devices and creating a vast network of interconnected systems. This interconnectedness, while offering numerous benefits, also introduces significant security vulnerabilities. Protecting IoT systems from malicious actors is crucial to ensure the reliability, safety, and trustworthiness of these increasingly important technologies.The evolving landscape of IoT security demands proactive measures to mitigate potential threats.
Addressing these security concerns requires a multifaceted approach encompassing robust device design, secure network protocols, and user awareness. The increasing complexity of IoT deployments, coupled with the growing sophistication of cyberattacks, necessitates a shift towards more comprehensive and adaptive security strategies.
Significant Security Threats in 2025
The expanding IoT ecosystem introduces numerous vulnerabilities. Attackers can exploit weaknesses in device firmware, network protocols, and communication channels to gain unauthorized access to sensitive data or disrupt operations. Sophisticated attacks targeting the interconnected nature of IoT systems, like distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks, will pose a considerable threat. Furthermore, the increasing use of artificial intelligence (AI) in IoT systems introduces new avenues for attack, as malicious actors may exploit vulnerabilities in AI algorithms or data pipelines.
Importance of Data Encryption and Access Control
Data encryption is fundamental to securing IoT systems. Robust encryption methods are essential to protect sensitive data transmitted over networks. By encrypting data both in transit and at rest, the risk of unauthorized access and data breaches can be minimized. Implementing strong access control mechanisms is equally crucial. This involves restricting access to IoT devices and data based on user roles and permissions, preventing unauthorized users from accessing sensitive information or manipulating systems.
Furthermore, authentication methods must be secure and resilient to attacks.
Strategies for Securing IoT Devices
Implementing secure coding practices during the development phase is paramount. Employing secure development lifecycles (SDLCs) ensures that security is integrated into every stage of device creation. This includes thorough code reviews, vulnerability assessments, and penetration testing to identify and address potential security weaknesses before deployment. Employing secure communication protocols, such as TLS/SSL, is essential for safeguarding data transmission.
Moreover, devices should be regularly updated with security patches to mitigate known vulnerabilities.
IoT trends in 2025 are poised to be pretty interesting, with smart appliances becoming increasingly commonplace. One prime example of this is the rise of the skin care fridge, like the ones available at skin care fridge. These smart fridges are designed to maintain the optimal temperature for sensitive skincare products, thus improving user experience and product longevity.
This focus on smart, connected devices will undoubtedly shape the future of home appliances in the coming years.
Best Practices for Implementing Robust Security Measures
A multi-layered approach is essential for robust security. Employing strong passwords and multi-factor authentication (MFA) for device access can significantly enhance security. Regularly updating firmware and software with security patches is critical. Employing intrusion detection and prevention systems (IDS/IPS) to monitor network traffic and identify suspicious activity can effectively detect and mitigate potential threats. Implementing security information and event management (SIEM) solutions for centralized log analysis is also crucial for identifying and responding to security incidents promptly.
Furthermore, promoting user awareness through security training and education is a key element in preventing social engineering attacks.
- Regular security audits and penetration testing to identify and address vulnerabilities are essential.
- Employing a Zero Trust security model, where no implicit trust is given to any device or user, is highly recommended.
- Implementing a secure update mechanism for firmware updates is crucial to mitigate vulnerabilities.
- Employing hardware security modules (HSMs) for cryptographic operations enhances the overall security of the IoT system.
IoT in Specific Industries
The convergence of Internet of Things (IoT) with various industries is transforming operational efficiency and customer experiences. Predictive maintenance, enhanced monitoring, and automated processes are becoming increasingly prevalent. This evolution is expected to accelerate further in the coming years, with specific applications tailored to the unique needs of each sector.The adoption of IoT technology is no longer a futuristic concept but a present reality, significantly impacting sectors like healthcare, agriculture, manufacturing, and retail.
The anticipated applications and trends in these industries reflect a continuous push for greater automation, data-driven decision-making, and enhanced user experiences.
IoT Trends in the Healthcare Industry in 2025
The healthcare industry will see significant advancements in remote patient monitoring and personalized medicine through IoT. Wearable sensors and implantable devices will gather detailed health data, allowing for proactive interventions and early detection of potential issues. This data will be analyzed by sophisticated algorithms to provide personalized treatment plans and improve patient outcomes.
- Remote patient monitoring systems will provide real-time health data to healthcare providers, enabling timely interventions and reducing hospital readmissions.
- Smart hospitals will utilize IoT devices for efficient resource management, such as automated medication dispensing and optimized bed allocation.
- Personalized medicine will leverage IoT data to tailor treatment plans to individual patient needs, enhancing treatment efficacy and reducing adverse reactions.
- Telemedicine will become more accessible, utilizing IoT devices to facilitate remote consultations and diagnostics, expanding access to healthcare in underserved areas.
Smart Agriculture Industry Utilizing IoT in 2025
Precision agriculture will be a driving force in the smart agriculture industry in 2025. IoT-enabled sensors will monitor soil conditions, weather patterns, and crop health, enabling farmers to optimize resource utilization and enhance yield. This data-driven approach will result in increased productivity and reduced environmental impact.
- Automated irrigation systems will adjust water usage based on real-time soil moisture data, conserving water resources and optimizing crop growth.
- Predictive maintenance of agricultural machinery will reduce downtime and improve operational efficiency.
- Smart sensors will detect and monitor pest infestations, enabling timely interventions to minimize crop damage and maximize yields.
- Livestock monitoring systems will track animal health and well-being, optimizing feeding and care practices.
Predicted Applications of IoT in the Manufacturing Sector in 2025
The manufacturing sector will leverage IoT for predictive maintenance, quality control, and supply chain optimization. Smart factories will utilize connected machines and sensors to anticipate equipment failures and optimize production processes. This will lead to increased efficiency, reduced downtime, and improved product quality.
- Predictive maintenance will identify potential equipment failures before they occur, minimizing downtime and reducing maintenance costs.
- Real-time monitoring of production processes will allow for immediate adjustments to optimize efficiency and quality.
- Automated quality control systems will ensure consistent product quality through real-time data analysis and feedback loops.
- Supply chain visibility will improve through connected devices and tracking systems, enabling better inventory management and reduced lead times.
IoT Use Cases in the Retail Industry in 2025
Retailers will use IoT to personalize customer experiences, optimize inventory management, and enhance store operations. Smart shelves and inventory tracking systems will provide real-time insights into product availability, enabling proactive restocking and improved customer service. Personalized recommendations and targeted promotions will further enhance the customer experience.
- Smart shelves will automatically track inventory levels, notifying staff of low stock and prompting automated restocking.
- Real-time customer tracking will allow retailers to personalize in-store experiences, offering targeted promotions and recommendations based on individual preferences.
- Smart fitting rooms will enhance the shopping experience, providing personalized recommendations and size suggestions.
- Enhanced security systems will use IoT devices to deter theft and monitor store operations.
Connectivity and Infrastructure for IoT

The increasing proliferation of interconnected devices in the IoT landscape necessitates robust and reliable communication infrastructure. Efficient data transmission and seamless connectivity are crucial for the effective functioning of IoT applications, enabling real-time insights and automation. Advancements in communication protocols and network technologies are pivotal in supporting the growth and sophistication of IoT deployments.
Expected Advancements in Communication Protocols
Communication protocols underpin the smooth flow of data in IoT systems. In 2025, we anticipate a continued evolution towards more energy-efficient, secure, and high-bandwidth protocols. Low-power wide-area networks (LPWANs) will likely see enhanced capabilities, facilitating long-range communication with minimal power consumption. The adoption of more sophisticated protocols like MQTT (Message Queuing Telemetry Transport) for device-to-cloud communication is expected to rise, due to its suitability for handling large volumes of data from diverse sources.
IoT trends in 2025 are looking pretty interesting, with smart home devices likely to become even more sophisticated. This increased connectivity also opens up exciting possibilities for personalized skincare routines, like using data to tailor face oils for dry skin face oils for dry skin to individual needs. Ultimately, this integration of technology will lead to more intuitive and efficient solutions in various sectors, including personal care.
Moreover, advancements in cellular technologies, particularly 5G and beyond, will play a significant role in bolstering the speed and reliability of IoT connectivity.
Impact of 5G and Advanced Networks on IoT Deployment
The introduction of 5G networks and subsequent advancements will dramatically reshape IoT deployment. 5G’s enhanced speed, low latency, and massive connectivity capabilities will enable real-time data analysis and control, crucial for applications requiring immediate responses, such as autonomous vehicles and industrial automation. Moreover, 5G’s ability to support a vast number of connected devices will unlock the potential of large-scale IoT deployments in various industries, including smart cities and agriculture.
Other advanced networking technologies, such as satellite communication systems, will further expand the reach of IoT deployments, especially in remote or underserved areas.
Challenges in Deploying and Maintaining Reliable IoT Infrastructure
Deploying and maintaining a reliable IoT infrastructure faces several significant challenges. Ensuring seamless connectivity across diverse environments, managing the sheer volume of data generated by connected devices, and addressing security vulnerabilities are key concerns. Furthermore, the heterogeneous nature of IoT devices and their varying communication requirements necessitates flexible and scalable infrastructure solutions. The ongoing need for reliable power sources, particularly in remote deployments, poses another significant hurdle.
Data privacy and security concerns, coupled with the complexity of managing and securing large-scale IoT networks, will also require careful consideration.
Communication Protocols and Suitability for IoT Applications
| Communication Protocol | Suitable IoT Applications | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Wi-Fi | Smart homes, short-range sensors, indoor asset tracking | High speed, widely available infrastructure | Limited range, higher power consumption |
| Bluetooth | Wearable devices, short-range sensors, personal devices | Low power consumption, short-range | Limited range, slower speed compared to Wi-Fi |
| Zigbee | Smart homes, industrial automation, building automation | Low power consumption, low cost, mesh networking | Limited speed, not suitable for high-bandwidth applications |
| LoRaWAN | Asset tracking, environmental monitoring, smart agriculture | Long range, low power consumption, cost-effective | Lower data rate, limited bandwidth |
| Cellular (5G, LTE) | Real-time monitoring, high-bandwidth applications, remote sensing | High bandwidth, wide range, ubiquitous infrastructure | Higher power consumption, costlier than LPWANs |
The table above highlights a variety of communication protocols and their applicability across diverse IoT applications. Choosing the right protocol is crucial for optimizing performance and ensuring the effectiveness of the IoT system in its specific environment.
Data Management and Analytics in IoT: IoT Trends 2025
The explosion of IoT devices generates massive amounts of data, demanding sophisticated data management systems. This data, if properly harnessed, offers invaluable insights into operational efficiency, predictive maintenance, and customer behavior. Consequently, effective data management and analytics are crucial for unlocking the full potential of IoT applications.
Evolution of Data Management Systems
IoT data management systems are evolving to accommodate the sheer volume, velocity, and variety of data generated. Traditional database systems are being augmented or replaced with specialized platforms designed for big data, including cloud-based solutions. These systems leverage distributed architectures, enabling faster data processing and storage. Furthermore, data lakes, which store raw data in its native format, are becoming increasingly prevalent, allowing for flexible analysis and exploration.
The flexibility of these systems allows for future expansion and incorporation of new data types.
AI and Machine Learning in IoT Analytics
AI and machine learning are revolutionizing data analytics for IoT systems. Algorithms are being deployed to identify patterns, anomalies, and trends within the vast datasets. This facilitates predictive maintenance, enabling proactive interventions before equipment failures occur. AI-powered insights can also personalize user experiences, optimize energy consumption, and improve supply chain management. Examples include predictive maintenance in manufacturing, where AI can forecast equipment failures, and smart agriculture, where AI analyzes sensor data to optimize irrigation and fertilization.
Real-Time Data Analysis in IoT Applications
Real-time data analysis is becoming a critical aspect of IoT applications. The ability to process data as it’s generated allows for immediate responses to events, enabling dynamic adjustments and optimized resource allocation. This is particularly valuable in applications such as smart traffic management, where real-time data on traffic flow can be used to adjust traffic signals and reduce congestion.
Other examples include remote patient monitoring, where real-time health data can be analyzed to detect potential health issues, and smart grids, where real-time energy consumption data can be used to optimize energy distribution.
Data Security and Privacy in IoT
Securing and protecting the privacy of data from IoT devices is paramount. Robust encryption protocols and secure communication channels are essential to prevent unauthorized access and data breaches. Furthermore, data anonymization and pseudonymization techniques can be employed to protect sensitive information while still enabling valuable analysis. Data access control and user authentication protocols are also critical. This requires a layered approach encompassing device-level security, network security, and data storage security.
Furthermore, compliance with data privacy regulations like GDPR and CCPA is vital. For instance, secure gateways that filter data before it reaches the cloud are crucial for protecting IoT devices and the sensitive information they collect.
The Role of AI in IoT
Artificial intelligence (AI) is poised to revolutionize the Internet of Things (IoT) landscape in 2025, driving greater automation, enhanced data analysis, and improved decision-making across diverse applications. AI’s ability to learn from vast amounts of data generated by interconnected devices enables intelligent systems that adapt and optimize themselves in real-time. This dynamic interaction between AI and IoT will create more efficient, responsive, and insightful solutions for businesses and consumers alike.
AI-Driven Automation in IoT
AI is enabling significant automation in IoT systems, leading to increased efficiency and reduced human intervention. Sophisticated algorithms analyze data from connected devices, triggering automated responses to various events. For instance, smart factories can optimize production lines based on real-time sensor data, adjusting machinery settings and resource allocation automatically to maximize output and minimize downtime. Predictive maintenance, another crucial application, uses AI to anticipate equipment failures, enabling proactive maintenance schedules and preventing costly disruptions.
Intelligent Decision-Making with IoT and AI
AI algorithms analyze the complex data streams generated by IoT devices to identify patterns, trends, and anomalies. This analysis facilitates intelligent decision-making in various domains. For example, in agriculture, AI-powered IoT systems can monitor soil conditions, weather patterns, and crop health, providing farmers with insights for optimized irrigation, fertilization, and pest control. This leads to increased yields and reduced resource consumption.
Similarly, in urban environments, smart city applications utilize AI to manage traffic flow, optimize energy consumption, and enhance public safety.
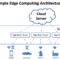
Edge Computing for Real-time IoT Data Processing
Processing data from IoT devices close to the source, rather than sending it to a centralized location for analysis, is crucial for real-time applications. Edge computing, a key component of this strategy, allows for faster data processing and reduced latency. By performing computations at the edge, IoT devices can react to events in real-time, enabling faster responses and improved responsiveness.
This is especially important in applications like autonomous vehicles, where quick decision-making is essential.
AI’s Impact on IoT Scalability and Maintainability
AI enhances the scalability and maintainability of IoT solutions by automating tasks and optimizing resource allocation. AI-powered systems can easily adapt to new devices and data streams, making it easier to expand and integrate new functionalities into existing IoT infrastructures. Moreover, AI algorithms can identify potential maintenance issues and predict equipment failures, facilitating proactive maintenance and reducing downtime.
This proactive approach to maintenance minimizes costly repairs and ensures consistent performance of IoT systems.
Impact on Business and Society
The pervasive integration of Internet of Things (IoT) technology promises substantial transformations across industries and society. This section explores the anticipated economic and societal impacts, including job implications and ethical considerations, highlighting the potential benefits and challenges of this transformative technology.
Potential Economic Impacts
The widespread adoption of IoT in 2025 is projected to drive significant economic growth across various sectors. IoT-enabled automation and optimization in manufacturing, logistics, and agriculture are anticipated to enhance productivity and reduce operational costs. Smart cities, for example, can optimize resource allocation and reduce energy consumption, leading to substantial cost savings for municipalities. Moreover, new business models centered around data-driven insights and personalized services will emerge, creating new revenue streams and opportunities for innovation.
This, in turn, is expected to fuel economic development and create jobs in related fields.
Societal Implications
The pervasive adoption of IoT in daily life will fundamentally alter societal structures and interactions. Connected homes and smart cities will enhance convenience and safety, while connected healthcare systems will enable proactive and personalized medical care. However, challenges such as data privacy, security, and the digital divide need careful consideration to ensure equitable access and responsible use. The potential for social stratification based on access to IoT technology and digital literacy also requires attention.
Job Creation and Displacement
The rise of IoT will likely lead to both job creation and displacement. New roles will emerge in areas like IoT system design, data analytics, and cybersecurity. The automation of certain tasks through IoT-enabled systems may lead to job displacement in traditional sectors, particularly those involving repetitive manual labor. Upskilling and reskilling initiatives will be crucial to adapt the workforce to the changing job market.
For instance, the development and maintenance of smart city infrastructure will require specialized personnel, while the analysis of massive IoT datasets will create opportunities for data scientists and analysts.
Ethical Considerations, IoT trends 2025
The increasing interconnectedness of devices raises significant ethical concerns. Issues surrounding data privacy, security, and algorithmic bias need careful consideration. The potential for misuse of personal data, the vulnerability of interconnected systems to cyberattacks, and the ethical implications of autonomous systems require robust regulations and ethical frameworks. For example, the deployment of autonomous vehicles raises concerns about liability in accidents, while the collection and use of personal data from smart homes raise concerns about privacy violations.
Clear guidelines and ethical frameworks are crucial for ensuring the responsible development and deployment of IoT technology.
Global Adoption of IoT
The global Internet of Things (IoT) landscape is poised for significant growth in 2025. Businesses across various sectors are increasingly recognizing the transformative potential of connected devices and systems, leading to a surge in deployment and adoption. This expansion is not uniform, however, with varying levels of penetration across different regions and industries. Understanding the drivers, challenges, and strategies for global adoption is crucial for organizations seeking to leverage the full potential of IoT.
Comparative Analysis of IoT Adoption Rates
The rate of IoT adoption varies significantly across countries in 2025. Developed nations like the United States, Canada, and many European countries typically exhibit higher adoption rates due to factors like robust infrastructure, established digital ecosystems, and a higher concentration of tech-savvy businesses. Emerging economies, while showing rapid growth, may lag behind in terms of overall adoption, influenced by infrastructure limitations, varying levels of digital literacy, and economic conditions.
For example, South Korea, known for its strong technological infrastructure, might have a higher IoT adoption rate compared to a less developed African nation. Precise figures on adoption rates will depend on specific industry sectors and data collection methodologies.
Key Market Factors Driving IoT Adoption
Several factors are driving the global adoption of IoT technologies. These include the need for increased operational efficiency, the desire for improved customer experiences, and the potential for generating valuable data-driven insights.
| Market Factor | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Cost Reduction | IoT implementation can lead to significant cost savings through automation, predictive maintenance, and optimized resource allocation. |
| Improved Efficiency | Connected devices can automate tasks, streamline processes, and optimize workflows, leading to increased efficiency in various operations. |
| Enhanced Security | IoT devices and systems can be designed to integrate advanced security protocols, mitigating vulnerabilities and improving overall data protection. |
| Data-Driven Insights | The vast amount of data generated by IoT devices can be analyzed to provide valuable insights, enabling better decision-making and strategic planning. |
| Competitive Advantage | Businesses leveraging IoT technologies can gain a competitive edge by improving their products, services, and operational processes. |
Factors Influencing Global Rollout
The global rollout of IoT technologies is influenced by a complex interplay of factors. These include technological advancements, supportive government policies, and the availability of skilled professionals. Furthermore, the reliability and security of communication networks are essential components for a successful rollout.
- Technological Advancements: Continuous innovation in sensor technology, communication protocols, and data analytics tools accelerates IoT deployment. Examples include the development of more energy-efficient sensors and the emergence of new, more secure communication protocols.
- Government Policies: Supportive government policies, including regulations and funding initiatives, can stimulate IoT adoption by fostering a conducive environment for businesses to invest and innovate. This could include initiatives aimed at improving digital infrastructure or providing incentives for IoT development.
- Infrastructure: The availability and reliability of communication infrastructure, including broadband networks and cellular connections, are vital for supporting IoT deployments. Regions with poor infrastructure may experience challenges in deploying and maintaining IoT systems effectively.
Strategies for Overcoming Challenges
Several strategies can help overcome the challenges associated with global IoT adoption. These include fostering collaborations between businesses and research institutions, promoting digital literacy programs, and developing standardized protocols for data exchange and security.
- Collaboration and Knowledge Sharing: Facilitating collaborations between businesses, research institutions, and government agencies can accelerate the development and deployment of IoT technologies. Joint research projects and knowledge-sharing platforms can foster innovation and address common challenges.
- Digital Literacy Programs: Investing in digital literacy programs can equip individuals with the necessary skills to effectively utilize and manage IoT technologies. This will create a workforce capable of designing, deploying, and maintaining complex IoT systems.
- Standardization: Developing standardized protocols for data exchange and security can enhance interoperability between different IoT systems. This will enable seamless integration and prevent fragmentation across various sectors and geographies.
Illustrative Examples and Case Studies
The proliferation of IoT devices is rapidly transforming industries and daily life. Understanding successful deployments and real-world applications is crucial for grasping the potential and challenges of this technology. This section presents illustrative examples and case studies, showcasing innovative applications across various sectors.
Successful IoT Deployments in 2025
Numerous organizations are leveraging IoT for enhanced efficiency and cost savings. In manufacturing, predictive maintenance using sensors on machinery allows proactive repairs, minimizing downtime and increasing output. Smart agriculture utilizes soil moisture sensors and weather data to optimize irrigation, maximizing crop yields and minimizing water usage. Retailers employ smart shelves to track inventory and automatically re-order products, enhancing supply chain management.
Innovative IoT Applications Across Industries
IoT applications are rapidly diversifying across numerous industries. A significant driver of this evolution is the integration of various data sources, which provides a holistic view of operations. This data-driven approach leads to better decision-making, optimized processes, and enhanced customer experiences.
| Industry | Application | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Smart Agriculture | Precision Irrigation | IoT sensors monitor soil moisture, weather patterns, and crop health. This data is used to optimize irrigation schedules, reducing water waste and maximizing crop yields. This can significantly impact agricultural efficiency and sustainability. |
| Retail | Smart Inventory Management | IoT-enabled smart shelves track inventory levels in real-time. Automated re-ordering systems ensure products are always available, minimizing stockouts and maximizing sales. This system helps improve supply chain efficiency and customer satisfaction. |
| Healthcare | Remote Patient Monitoring | Wearable devices and home sensors track vital signs and activity levels. Real-time data transmission allows healthcare professionals to monitor patients remotely, enabling timely interventions and proactive care. This leads to better patient outcomes and reduced hospital readmissions. |
| Manufacturing | Predictive Maintenance | Sensors embedded in machinery monitor performance parameters. Data analysis identifies potential failures before they occur, enabling proactive maintenance and minimizing downtime. This approach improves equipment reliability and reduces maintenance costs. |
Detailed Descriptions of Real-World IoT Applications
A key application is remote patient monitoring in healthcare. Wearable devices and home sensors track vital signs, activity levels, and other health data. This data is transmitted to healthcare providers, enabling timely interventions and proactive care, ultimately improving patient outcomes and reducing hospital readmissions. Another example is the use of smart lighting systems in urban environments. These systems adjust lighting levels based on ambient conditions and occupancy, reducing energy consumption and improving public safety.
Impact of IoT on Everyday Life in 2025
The impact of IoT on daily life in 2025 will be profound. Smart homes will automatically adjust temperature, lighting, and security settings based on occupancy and preferences. Personalized recommendations for shopping and entertainment will be tailored to individual needs. Smart cities will optimize traffic flow, reduce congestion, and improve public safety. These examples illustrate the transformative impact of IoT on daily routines.
Final Thoughts
In conclusion, IoT trends in 2025 are poised to significantly reshape various industries and daily life. The emergence of new technologies, evolving security standards, and the expanding use cases across industries underscore the importance of understanding the intricate interplay of these factors. This exploration provides a comprehensive view, highlighting the challenges and opportunities presented by this transformative technology.
FAQ
What are some emerging technologies impacting IoT in 2025?
Several emerging technologies are expected to significantly impact IoT in 2025, including advancements in AI, 5G, and edge computing, among others. These will transform existing applications and create new opportunities across diverse industries.
What are the key security threats facing IoT devices and networks in 2025?
IoT devices are vulnerable to various security threats, including hacking, data breaches, and denial-of-service attacks. Robust security measures are crucial for protecting sensitive data and maintaining the integrity of these systems.
How will data management systems evolve to accommodate the massive data volumes from IoT devices?
Data management systems will need to adapt to handle the exponentially growing data volume generated by IoT devices. This involves improving data storage capacity, processing speed, and efficient data analytics capabilities.
What are the ethical considerations surrounding IoT technology?
As IoT adoption increases, ethical considerations regarding privacy, security, and the potential for misuse of data need careful attention. The societal impact of widespread IoT integration must be thoughtfully addressed.